Discussion on Laser Cutting Technology
Release Date:2025/04/24
Definition of laser cutting
▼What is laser?
Laser is an enhanced light obtained by stimulated radiation, and its basic characteristics are:High intensity, high brightness, wavelength frequency determination, good monochromaticity, good coherence, long coherence length, good directionality, almost a beam of parallel light.
High intensity, high brightness, wavelength frequency determination, good monochromaticity, good coherence, long coherence length, good directionality, almost a beam of parallel light. When the laser beam is irradiated onto the surface of the workpiece, the light energy is absorbed and converted into heat energy, causing the temperature at the irradiated spot to rapidly rise, melt, and vaporize, forming small pits. Due to thermal diffusion, the metal around the spot melts, and the metal vapor inside the small pit rapidly expands, producing a micro explosion that sprays out the molten material at high speed and generates a highly directional anti shock wave. As a result, a hole with a large top and a small bottom is drilled on the processed surface.
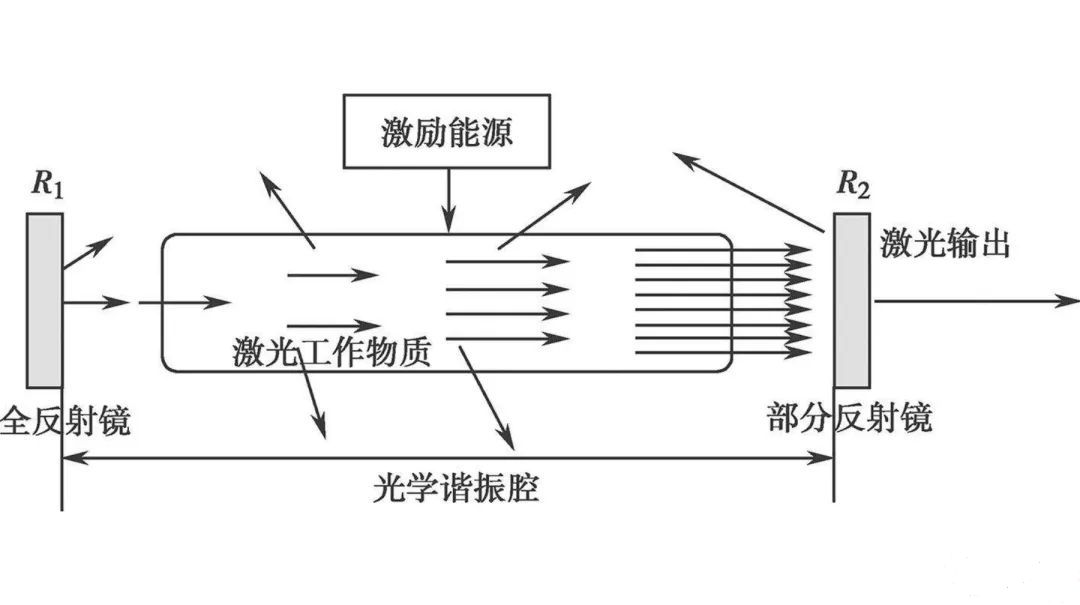
▼ Generation of laser

The generation of laser is achieved by reversing the number of particles in the working substance, generating photons through stimulated radiation, and amplifying and selecting modes of photons through an optical resonant cavity,The final output is a laser with high directionality, monochromaticity, coherence, and brightness.
▼The principle of laser cutting
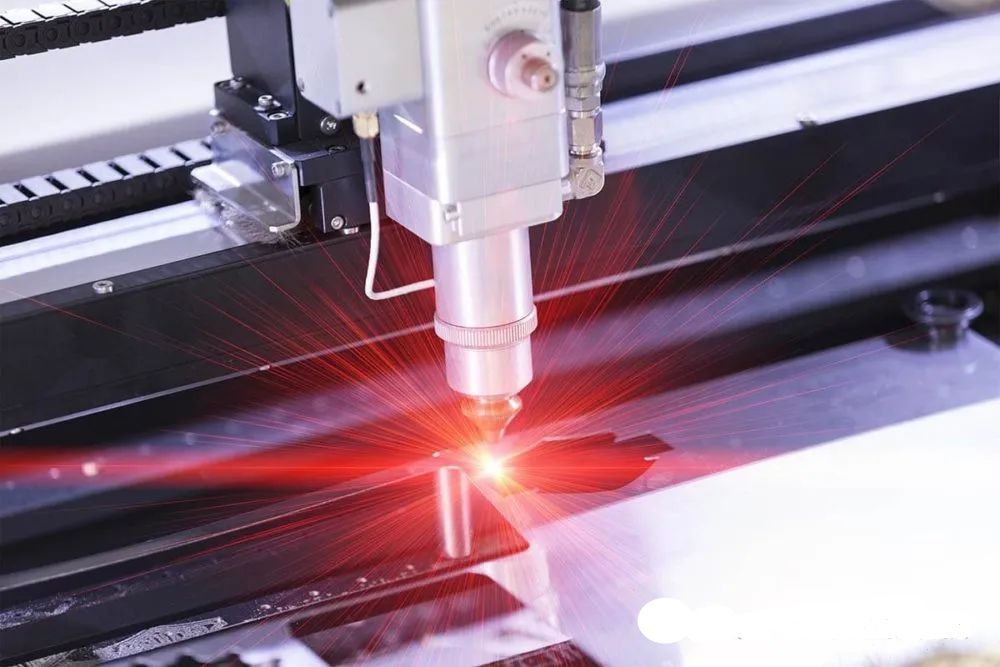
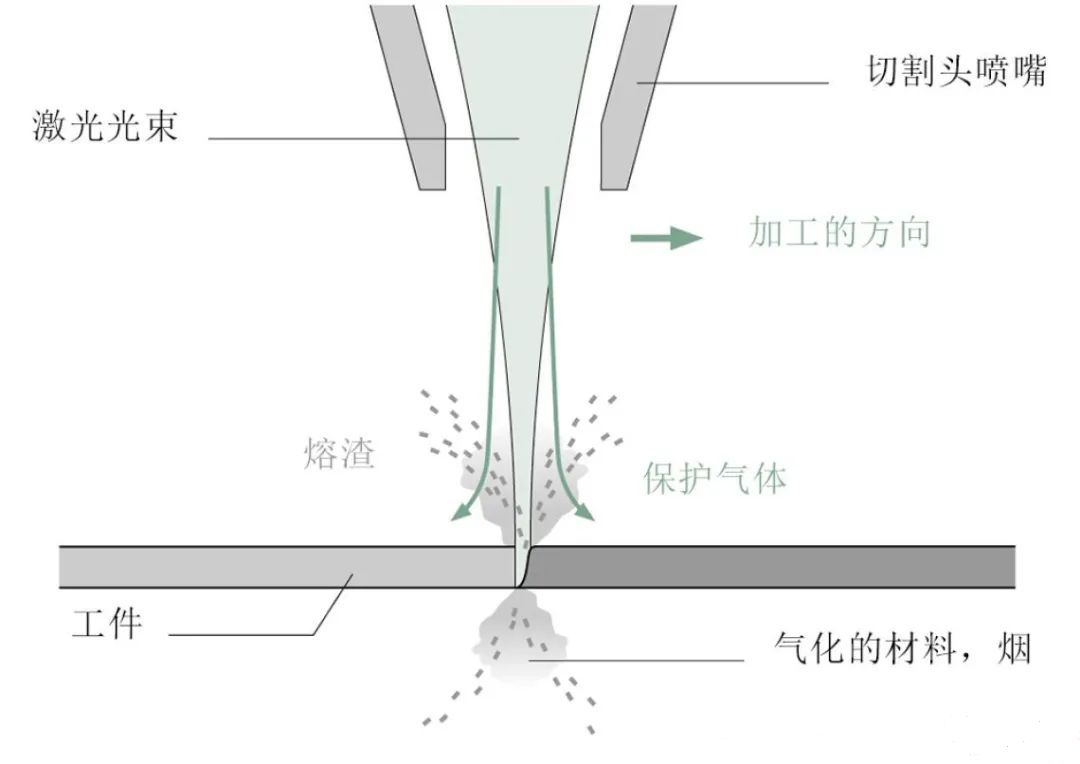
Laser cutting is a processing technique that uses a high-energy density laser beam as a heat source to cut materials.
After laser beam focusing, it has extremely high energy density. When it is irradiated onto the surface of the material, the material absorbs the energy of the laser, causing the temperature of the irradiated area to rise sharply, reaching the melting point, boiling point, and even direct sublimation of the material. For most metal materials, laser energy melts the metal, and auxiliary gases such as oxygen and nitrogen are used to blow the melted material away from the cutting seam, thereby achieving material separation; For some non-metallic materials such as wood, plastic, etc., laser energy may directly vaporize them, thereby completing cutting.
Characteristics of laser cutting
Compared with other thermal cutting methods, optical cutting has the overall characteristics of fast cutting speed and high quality. Specifically summarized in the following aspects.
(1) Good quality: Laser cutting has a narrow incision and a small heat affected zone. The heat affected zone refers to the area where a material undergoes changes in its structure and properties due to heat during the cutting process. The width of the heat affected zone generated by laser cutting is usually between 0.1-0.5mm, which is very important for some application scenarios that require high material performance, such as cutting metal components in the aerospace industry.
(2) High precision:Laser cutting can achieve high-precision cutting, with a cutting accuracy of about ± 0.1mm, which makes it widely used in precision machining fields such as electronic component manufacturing and medical device production. For example, in the manufacturing of mobile phone circuit boards, laser cutting can accurately cut out tiny circuits and component installation areas.
(3) Fast speed: Compared to traditional cutting methods such as mechanical cutting or flame cutting, laser cutting has a faster speed. For low-carbon steel plates with a thickness of 1-6mm, the laser cutting speed can reach several meters per minute, greatly improving production efficiency.
(4) Wide material adaptability: It can cut various materials, including metals (such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc.), non metals (such as ceramics, glass, rubber, etc.), and composite materials. Different materials can achieve good cutting effects by adjusting laser parameters and auxiliary gases.
(5) Non contact cutting: During laser cutting, there is no contact between the cutting torch and the workpiece, and there is no tool wear. Processing parts of different shapes does not require changing the "cutting tool", only changing the output parameters of the laser. The laser cutting process has low noise, minimal vibration, and no pollution.
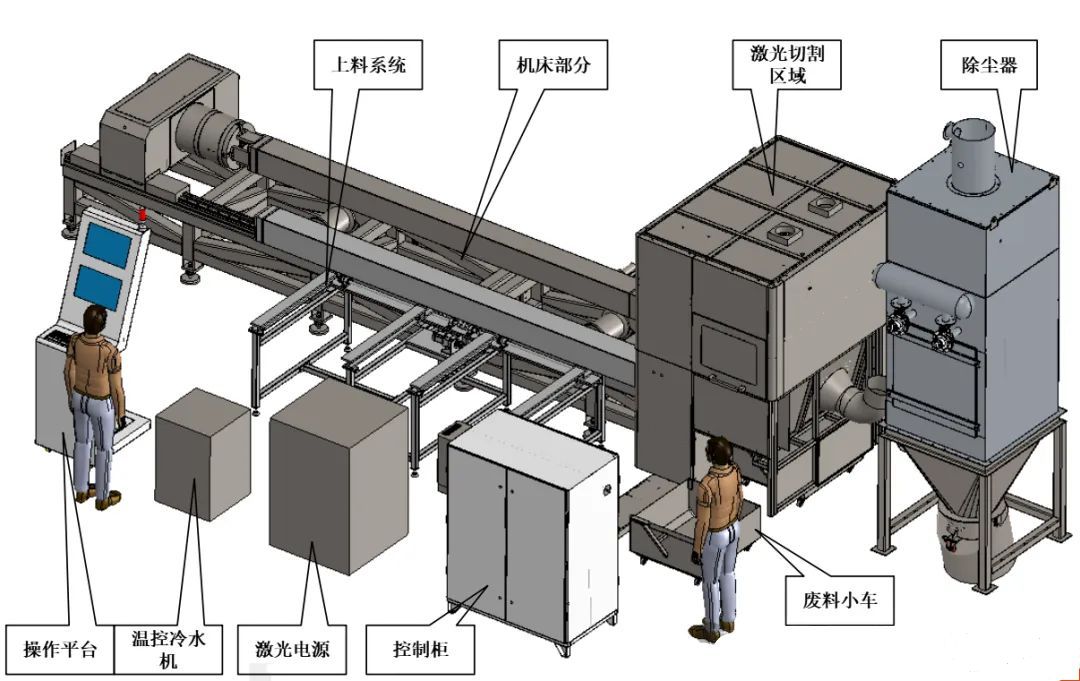
Due to the limitations of laser power and equipment volume, laser cutting can only cut medium to small thickness plates and pipes, and the cutting speed decreases significantly with the increase of workpiece thickness.
Application areas of laser cutting
Metal processing industry: widely used in metal processing, such as cutting automotive parts (body frames, engine components, etc.) in the automotive manufacturing field; Used for cutting steel plates and manufacturing ship structures in shipbuilding; Mechanical manufacturing is used for cutting various mechanical parts such as gears, shafts, etc.
Electronics industry: used for cutting circuit boards (PCBs), accurately separating circuit components, and can also be used for cutting metal or non-metal parts such as electronic device casings.
Advertising and decoration industry: cutting various advertising signs and decorative panels. For example, laser cutting can be used to create exquisite signage and decorative patterns made of materials such as stainless steel and acrylic, with precision and diversity that traditional processing methods cannot match.
Packaging industry: cutting packaging materials, such as paper boxes, plastic films, etc., and carving patterns on packaging materials to improve the beauty and personalization of packaging.
Aerospace field: used for cutting aerospace components, such as aircraft wings, fuselage frames and other structural parts, as well as some high-precision aircraft engine components, to ensure that the quality and performance of the components meet strict requirements.