Laser equipment industry research report: Welding technology iteration upgrade
Release Date:2025/04/27
Welding technology continues to upgrade and iterate, and intelligent welding robots integrate high-precision sensing devices such as visual sensors and laser sensors, combined with artificial intelligence algorithms to achieve real-time recognition of welds, automatic path generation, and dynamic optimization, greatly reducing reliance on manual teaching, promoting the comprehensive upgrade of intelligent manufacturing systems, and entering non-standard application scenarios.
Summary
Welding technology continues to upgrade and iterate, and intelligent welding robots have entered non-standard application scenarios. Intelligent welding robots integrate high-precision sensing devices such as visual sensors and laser sensors, combined with artificial intelligence algorithms to achieve real-time recognition of welds, automatic path generation, and dynamic optimization, greatly reducing reliance on manual teaching and promoting the comprehensive upgrade of intelligent manufacturing systems. Compared to traditional teaching robots, intelligent welding robots have shown outstanding advantages in non-standard welding fields such as precision electronic devices and lightweight automotive components, especially suitable for multi variety and small batch production scenarios.
The shortage of welders has spurred demand for substitution, and policies are promoting the accelerated popularization of intelligent welding from multiple perspectives. With the total shortage of welders in China approaching 3.49 million, and the combined proportion of welders born in the 1960s and 1970s exceeding 60%, the pressure of the industry's "shortage of talent" is becoming apparent. If one welding robot can replace 2.5 welders, the potential market space for intelligent welding robots is 1.4 million units. The country continues to release policy documents such as the "Implementation Opinions on Improving Manufacturing Reliability" and the "Industrial Equipment Renewal Plan" to accelerate the implementation of intelligent manufacturing and welding automation, and the penetration rate of welding robots is expected to increase rapidly.
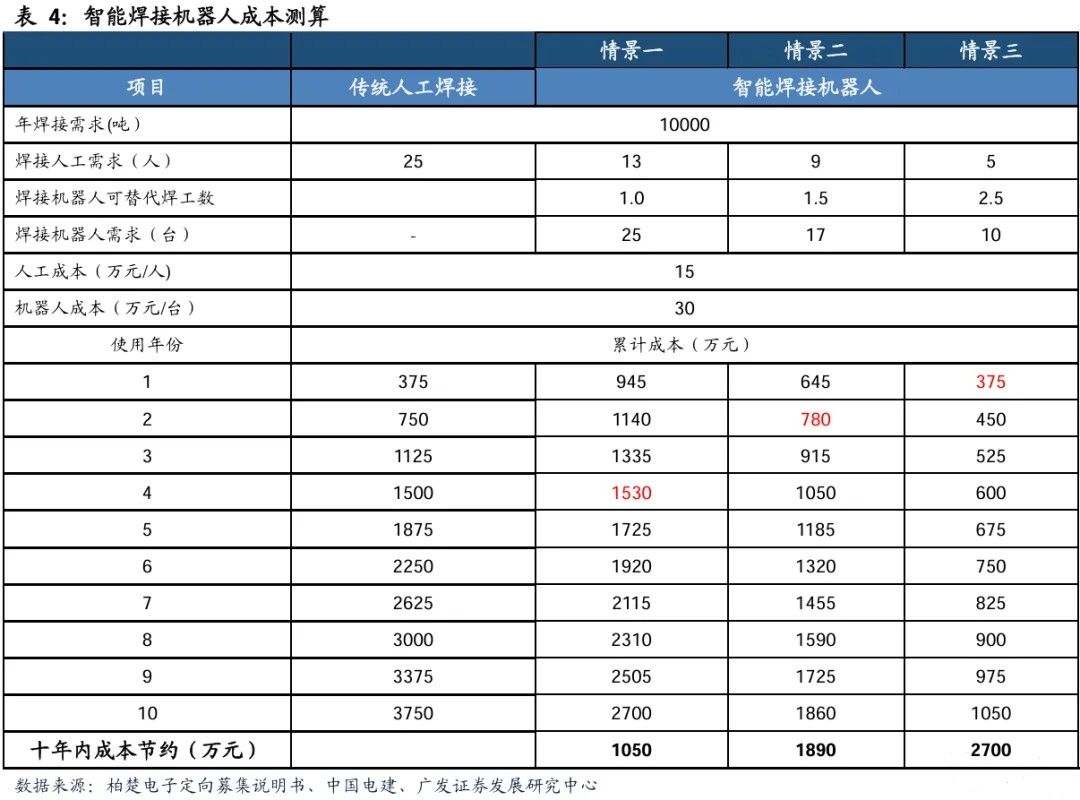
The cost-effectiveness advantage of machines replacing humans is highlighted, and the cost recovery cycle is short. According to the information from the Doctor of Engineering Intelligent Manufacturing Platform, the welding speed of intelligent robots is generally 50-160 cm/min, while the manual welding speed is 40-60 cm/min. Considering the differences in welding speed under different welding scenarios, we analyzed the worst-case scenario (i.e. one intelligent robot can only replace one welder), the general scenario (i.e. one robot can replace 1.5 welders), and the best scenario (i.e. one robot can replace 2.5 welders). The results show that even in the worst case scenario, using intelligent welding robots can cover the cost of manual welding within 4 years and save 10.5 million yuan within 10 years. In the best case scenario, using intelligent welding robots can cover costs in the first year and save up to 27 million yuan within a ten-year cycle.
The demand for non-standard welding scenarios is urgent, and the penetration of steel structures and ships is accelerating. According to data from the China Steel Structure Association, the national steel structure processing volume has reached 112 million tons in 2023, and the industry is currently facing pain points of low automation level and high dependence on manual labor. According to GGII, about 60% of the total steel structure processing requires intelligent welding. Shipbuilding also faces challenges such as complex weld structures and customized production in small batches, which has led to the emergence of robots to replace rigid needs. According to a report by Gaogong Robotics, there will be approximately 187800 certified welders from China Classification Society in 2024, indicating a vast demand for intelligent welding robots to replace them.
Risk Warning: Risks of policy implementation falling short of expectations, overall industrial and technological development falling short of expectations, and safety and economic risks falling short of expectations.
Main text
1、 Welding technology is constantly upgrading, and intelligent welding robots are the new direction
(1) Welding technology is a cornerstone of modern industry
Welding technology, as the cornerstone of modern industry, achieves atomic level bonding of materials through high temperature or pressure, and is widely used in core fields such as automobiles, aerospace, construction, and energy. Its accuracy and efficiency directly determine the structural strength and production cost of industrial products. For example, high-strength steel plate connections for car bodies, high-temperature welding for aircraft engines, and safe sealing of nuclear power plant pipelines all rely on welding technology to achieve reliability and large-scale production.
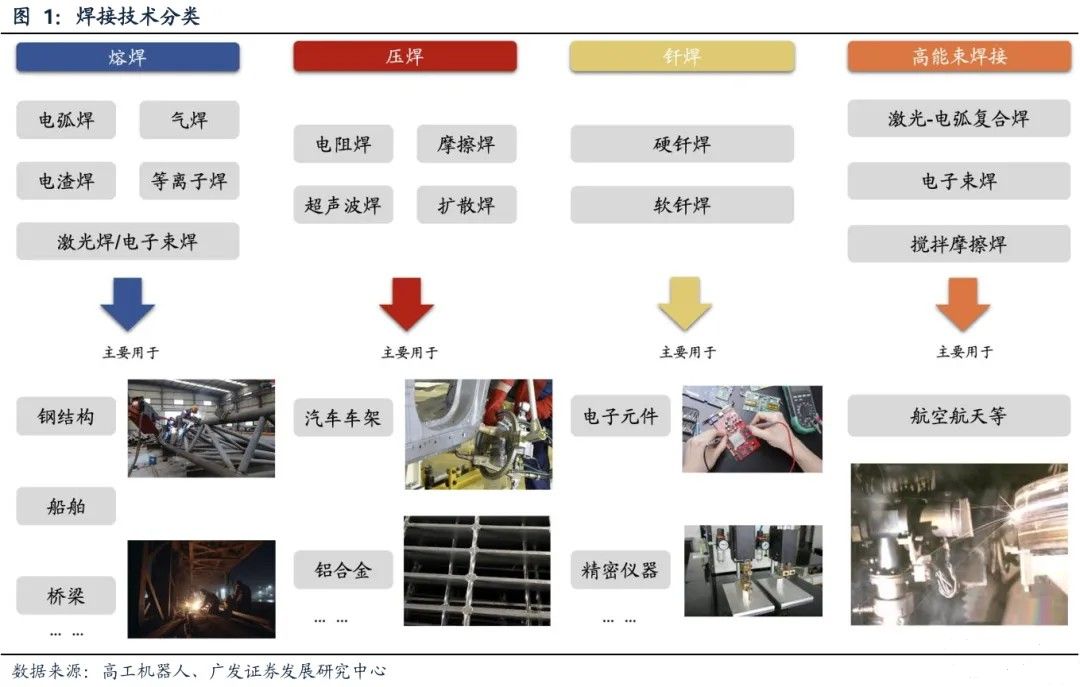
According to the differences in heat sources and processes, welding is mainly divided into three categories: fusion welding, pressure welding, and brazing. (1) Fusion welding achieves connection by melting the base material, such as arc welding (manual welding, submerged arc welding), which is suitable for steel structure construction and shipbuilding. (2) Pressure welding (such as resistance welding and friction welding) does not require filling materials and is commonly used for spot welding of automotive frames and processing of aluminum alloy sheets. (3) Brazing uses low melting point alloys to connect dissimilar materials, which is particularly critical in electronic components and precision instruments. In recent years, new technologies such as laser welding and electron beam welding have broken through traditional limitations. For example, the aerospace industry uses laser arc composite welding to achieve efficient deep penetration welding of titanium alloys, while the microelectronics industry relies on ultrasonic welding to achieve precise connection of chip leads.
Welding robots are modern industrial equipment that integrate multidisciplinary technologies. The welding robot consists of two parts: the robot body and the welding supporting equipment. The main body is centered around a six axis robotic arm, including key components such as a control system, precision reducer, and servo motor; Welding equipment includes welding power sources, specialized welding guns, and automatic wire feeding devices. This type of equipment can achieve high-precision and high stability automated welding by integrating artificial intelligence and sensor technology.
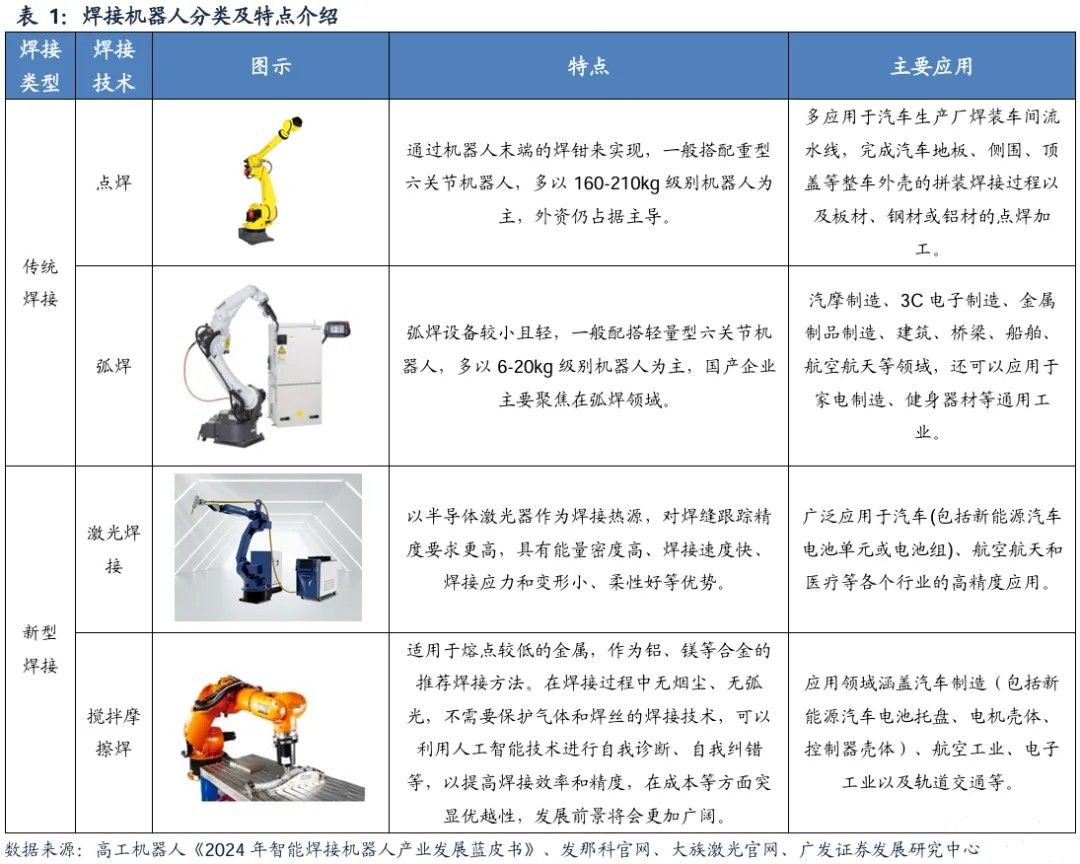
Welding robots can be divided into four mainstream types according to their processes, covering different industrial scenarios. According to data from Gaogong Consulting, spot welding and arc welding robots account for 90% of the market share. Spot welding robots are mainly used for thin plate welding in the automotive manufacturing industry, with typical applications including vehicle shell assembly, which requires the use of 160-210kg heavy-duty robotic arms. Currently, the market is still dominated by foreign-funded enterprises such as Fanuc and ABB. Arc welding robots are suitable for 6-20kg lightweight robotic arms and are widely used in fields such as automotive and motorcycle parts, 3C electronics, etc. due to their precise control ability over complex weld trajectories, becoming the main battlefield for domestic manufacturers to compete. In addition, new technologies such as laser welding and friction stir welding are accelerating their penetration into the fields of new energy vehicles and aerospace.
(2) Intelligent welding robot technology is becoming increasingly mature
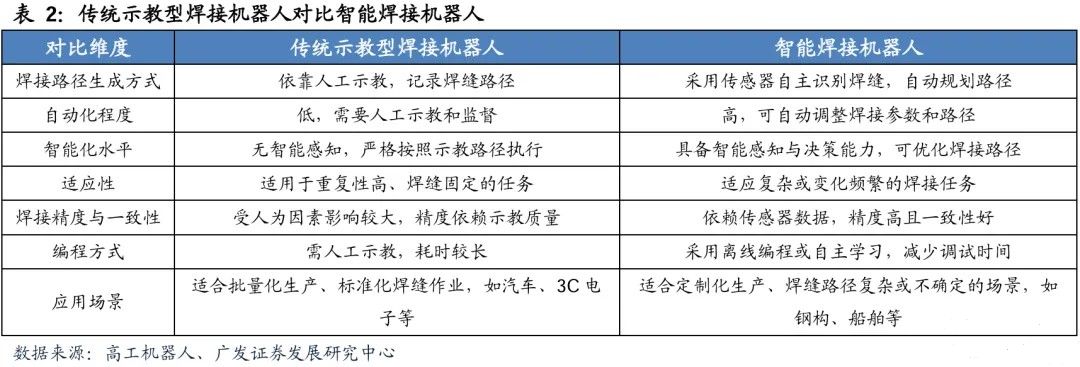
According to the different ways in which robot processing paths are generated, welding robots can be divided into two categories: traditional teaching robots and intelligent welding robots. Traditional teaching welding robots adopt a "teaching reproduction" mode, relying on manual guidance of the welding gun trajectory and recording of action parameters to form a fixed programmed welding path; Intelligent welding robots integrate high-precision sensing devices such as visual sensors and laser sensors, combined with artificial intelligence algorithms to achieve real-time recognition of welds, automatic path generation, and dynamic optimization, greatly reducing the dependence on manual teaching and significantly improving operational flexibility.
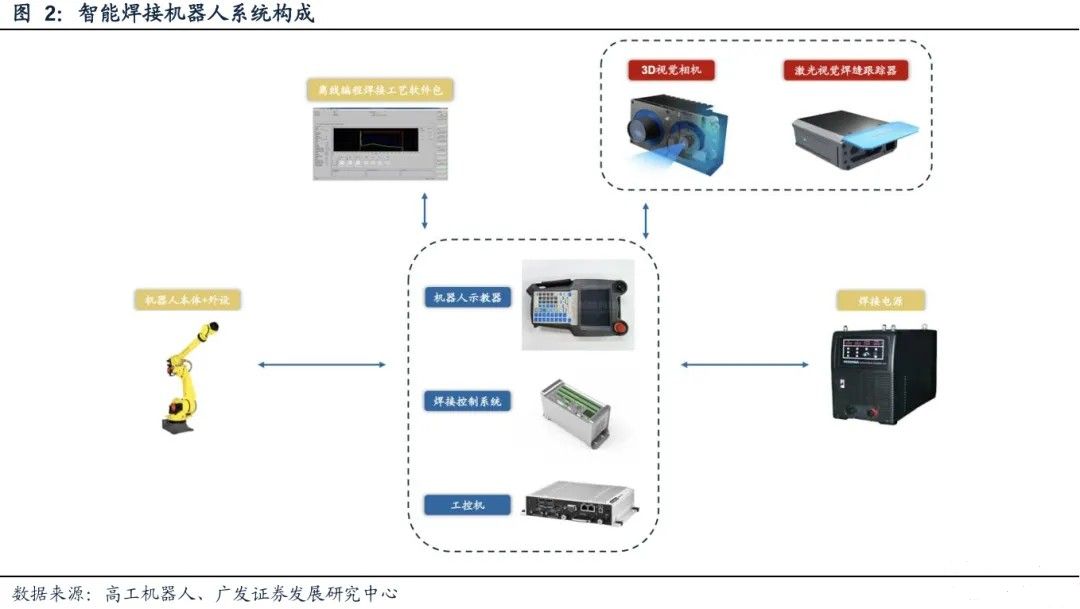
A complete intelligent welding robot system consists of an intelligent control system, a visual sensing and tracking module, an offline programming platform, and a robot body. Its core lies in the support of offline programming software: users can complete weld seam modeling, path planning, and process simulation in a virtual environment, automatically adjust welding current, speed, and other process parameters through preset parameters, and verify the rationality of the path, greatly shortening the debugging cycle. Compared to traditional models, intelligent robots have multidimensional advantages - deep learning based decision systems can optimize welding strategies in real-time based on material characteristics and workpiece deformation, high-precision sensors ensure millimeter level positioning stability, flexible design makes it compatible with multiple types of welding guns and process requirements, and reduces operational risks through safety protection mechanisms.
With the deep integration of artificial intelligence and IoT technology, intelligent welding robots are evolving from "semi autonomous" to "fully autonomous". Its technological breakthroughs are reflected in two aspects: one is to achieve online repair of welding defects and self iterative optimization of process parameters through reinforcement learning; The second is to use digital twin technology to construct a virtual real mapping system, further enhancing the adaptability of complex surface welding. Compared to traditional teaching robots, the intelligent version demonstrates outstanding advantages in non-standard welding fields such as precision electronic devices and lightweight automotive components, especially suitable for multi variety and small batch production scenarios. In the future, with the popularization of 5G remote control and edge computing technology, the welding robot will realize cross platform collaborative work and cloud knowledge sharing, and promote the comprehensive upgrade of intelligent manufacturing system.
Intelligent welding robots have made key breakthroughs, especially in 3D vision and weld seam recognition. In June 2024, an appraisal meeting organized by the Guangdong Mechanical Engineering Society confirmed that Ruiji Technology's "3D Vision Guided Non Teaching Welding Robot System" has broken the traditional reliance on teaching in automated welding and can achieve autonomous recognition and path planning in complex 3D environments. The expert system under its "cloud edge end" architecture supports flexible production of multiple varieties and small batches, significantly expanding the boundaries of automation applications and providing strong support for non standardized manufacturing environments.
Welding automation has become a key pivot for upgrading intelligent manufacturing. The rigid demand for high-quality and low-cost welding processes in industries such as ships, steel structures, and heavy equipment provides a practical foundation for the rapid popularization of intelligent welding robots. With the performance of domestic welding robots approaching international standards, leading enterprises are accelerating the formation of competitive advantages in the intelligent welding market through technological integration and industry chain collaboration.
2、 The gap for welders is large, and the space for intelligent welding robots is vast
(1) The shortage of welders continues to worsen, and policies are working together to promote robot substitution
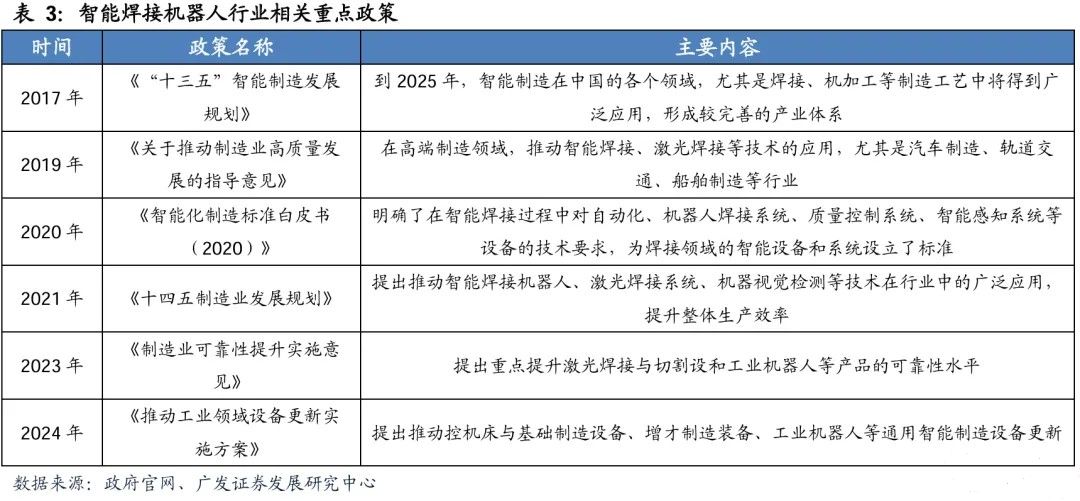
China's welding resources continue to be scarce, and the industry's demand for alternative solutions is becoming increasingly urgent. In the fourth quarter of 2022, welders ranked 12th in the national "most in demand" list. According to data from China Youth Daily, by 2024, there may be a shortage of 400000 senior welders in China, with an overall demand gap of 3.49 million welders. If one welding robot can replace 2.5 welders, the potential market space is 1.4 million units. At the same time, the aging age structure of welders is worsening, with a total of 61% of welders born in the 1960s and 1970s, while only 13% are born in the 1990s. The industry is facing the harsh reality of a shortage of young and old welders.
The harsh working environment and health risks of welding positions further exacerbate young people's alienation from the profession. High temperature, high noise, electromagnetic radiation, strong light, and dust pollution make welding work no longer attractive, despite the high salary level. In this context, the manufacturing industry is accelerating the introduction of intelligent and automated welding solutions to cope with talent shortages, improve welding quality and efficiency, and intelligent welding robots have become a key technological breakthrough for "machines replacing humans".
Policy support promotes the popularization of intelligent welding robots. Since the 13th Five Year Plan for the Development of Intelligent Manufacturing, the national level has continued to promote the widespread application of intelligent manufacturing in the welding process. Subsequently released documents such as the "Guiding Opinions on Promoting High Quality Development of Manufacturing Industry" and the "14th Five Year Plan for Manufacturing Industry Development" regard intelligent welding technology as the core means to enhance the modernization level of the industrial chain, and focus on supporting the industrialization landing of key industries such as automobiles, rail transit, and ships.
The government continues to improve the technical standard system and promote equipment upgrades. The 2020 White Paper on Intelligent Manufacturing Standards specifies the technical specifications for automated welding systems; The Implementation Opinions on Enhancing Manufacturing Reliability in 2023 focus on improving equipment reliability; The Implementation Plan for Promoting Equipment Renewal in the Industrial Sector in 2024 emphasizes accelerating the upgrading of intelligent manufacturing equipment. These policies constitute a stable and continuous policy environment, laying a solid foundation for the rapid development of the intelligent welding robot industry.
(2) Market demand is steadily increasing, and economic advantages are becoming increasingly prominent
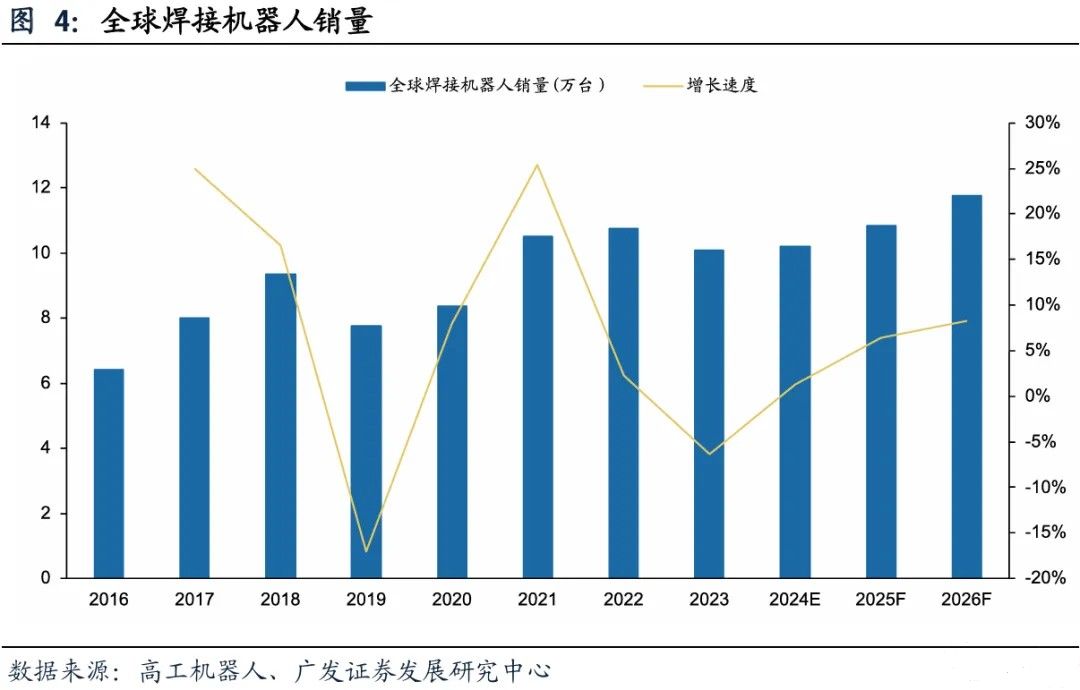
The global welding robot market is showing a steady growth trend. According to data from Gaogong Consulting, global sales of welding robots have increased from 64200 units to an estimated 102000 units from 2016 to 2024. The expected sales for 2025 and 2026 are 108500 and 117500 units respectively, with year-on-year growth of 6% and 8%. The industry has entered a stage of steady expansion.
The application of intelligent welding robots in the field of steel structures has formed significant economic benefits. According to the targeted fundraising prospectus of Baichu Electronics, Chinese welders can complete an average of 400 tons of welding tasks per year. Taking the steel structure production line with an annual output of 100000 tons as an example, manual welding requires 25 welders. If the intelligent welding system is fully adopted and combined with the practical experience of China Electric Power Construction, the work efficiency of a single robot can reach 1.5 times that of a skilled welder, and one operator can manage two devices at the same time. Based on an annual salary of 150000 yuan for welders and a machine cost of 300000 yuan, the cost can be saved by about 18.9 million yuan within a ten-year period.
Under different substitution efficiencies, robots still have a high return on investment. According to the information from the Doctor of Engineering Intelligent Manufacturing Platform, the welding speed of intelligent robots is generally 50-160 cm/min, while the manual welding speed is 40-60 cm/min. Considering the differences in welding speed under different welding scenarios, we analyzed the worst-case scenario (i.e. one intelligent robot can only replace one welder), the general scenario (i.e. one robot can replace 1.5 welders), and the best scenario (i.e. one robot can replace 2.5 welders). The results show that even in the worst case scenario, using intelligent welding robots can cover the cost of manual welding within 4 years and save 10.5 million yuan within 10 years. In the best case scenario, using intelligent welding robots can cover costs in the first year and save up to 27 million yuan within a ten-year cycle. In addition, welding robots can operate 24 hours a day without interruption, unaffected by factors such as fatigue and rest, significantly improving welding efficiency and ensuring the progress of the project as planned. This indicates that with the advancement of robot technology and changes in labor costs, the economy of intelligent welding is expected to further improve, and in the long run, its trend of replacing manual labor will become increasingly apparent.
(3) The non-standard welding market has a wide range of applications, and the penetration of steel structures and ships is accelerating
1. Analysis of the Steel Structure Industry
Under policy guidance, China's steel structure industry is accelerating its transformation towards high-end manufacturing. According to the "14th Five Year Plan and 2035 Long Range Objectives for the Steel Structure Industry" released in 2021, the country explicitly requires that the annual consumption of steel structures be increased to 140 million tons by 2025, and exceed 200 million tons by 2035, and fully realize intelligent construction. With policy support, the industry continues to expand in scale. According to data from the China Steel Structure Association, the national steel structure processing volume has reached 112 million tons in 2023, a year-on-year increase of 10.5%. However, the current industry still faces core challenges, such as low automation levels and high dependence on manual labor.
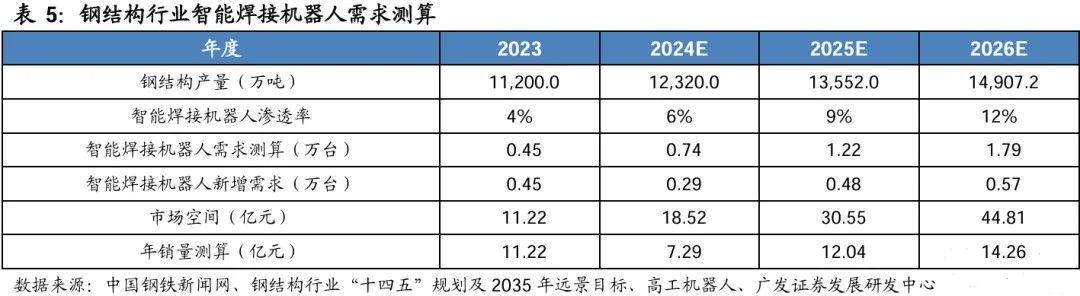
The contradiction between supply and demand is forcing the industry to accelerate its intelligent transformation. According to GGII, about 60% of the total steel structure processing requires intelligent welding. Referring to the previous estimation of the penetration rate of intelligent welding robots, combined with the industry standard of 10 devices per 10000 tons of steel, the steel structure production is expected to increase to 135 million tons by 2025, which will directly stimulate the demand for 12200 intelligent welding robots. According to the 2021 report by Bochu Electronics, the price of an intelligent welding robot workstation is approximately 280000 yuan per unit. In the long run, based on an average price of 250000 yuan per device, it is estimated that the market size will exceed 3 billion yuan by 2025. This growth logic is based on two core driving forces: a stable annual growth rate of 10% in steel structure production, and a rapid increase in intelligent penetration rate from the current less than 10% to the planned target, forming a dual growth curve of "scale expansion+technological substitution".
2. Analysis of the Shipbuilding Industry
The growth momentum of the shipbuilding industry is strong, and its global leading position is highlighted. The Chinese shipbuilding industry is entering a period of rapid development. According to data from the China Shipbuilding Industry Association, from January to December 2024, the national shipbuilding completion volume reached 48.18 million deadweight tons, a year-on-year increase of 13.8%; The newly received order volume was 113.05 million deadweight tons, a significant increase of 58.8% year-on-year; The volume of handheld orders exceeded 208 million deadweight tons, a year-on-year increase of 49.7%. The three core indicators account for over 50% of the global market share, reaching 55.7%, 74.1%, and 63.1% respectively in terms of deadweight tonnage, significantly consolidating China's leading position in the global shipbuilding industry. The expansion of the industry scale and the surge in orders have provided strong demand support for the upgrading of welding processes.
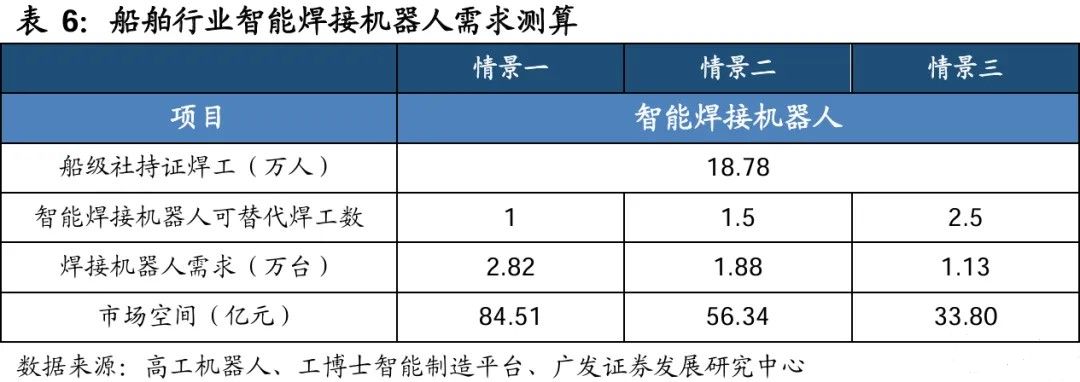
Shipbuilding is facing challenges such as complex weld structures and customized production in small batches. Traditional welding methods are difficult to adapt to, leading to the emergence of robots to replace rigid needs. Ship welds are short and diverse, with large assembly accuracy deviations; At the same time, the development of ship equipment towards ultra large and integrated sizes has intensified the contradiction between the insufficient efficiency and quality stability of manual welding. According to a report by Gaogong Robotics, there will be approximately 187800 certified welders from China Classification Society in 2024. Based on a penetration rate of 15% for intelligent welding robots and referring to the previous comparison of welding speed between intelligent welding robots and manual welding, we analyzed the worst-case scenario (i.e. one intelligent robot can only replace one welder), the general scenario (i.e. one robot can replace 1.5 welders), and the best scenario (i.e. one robot can replace 2.5 welders). The demand for intelligent welding robots in the shipbuilding industry is expected to reach 18800 units, creating a market space of 5.634 billion yuan. If we can accelerate the replacement of manual welding and further increase the penetration rate to 30%, it is expected to drive a market size of over 10 billion yuan, promote the transformation of shipbuilding industry towards high-end and green, and enhance the global industrial chain discourse power.
3、 Intelligent welding robot industry chain
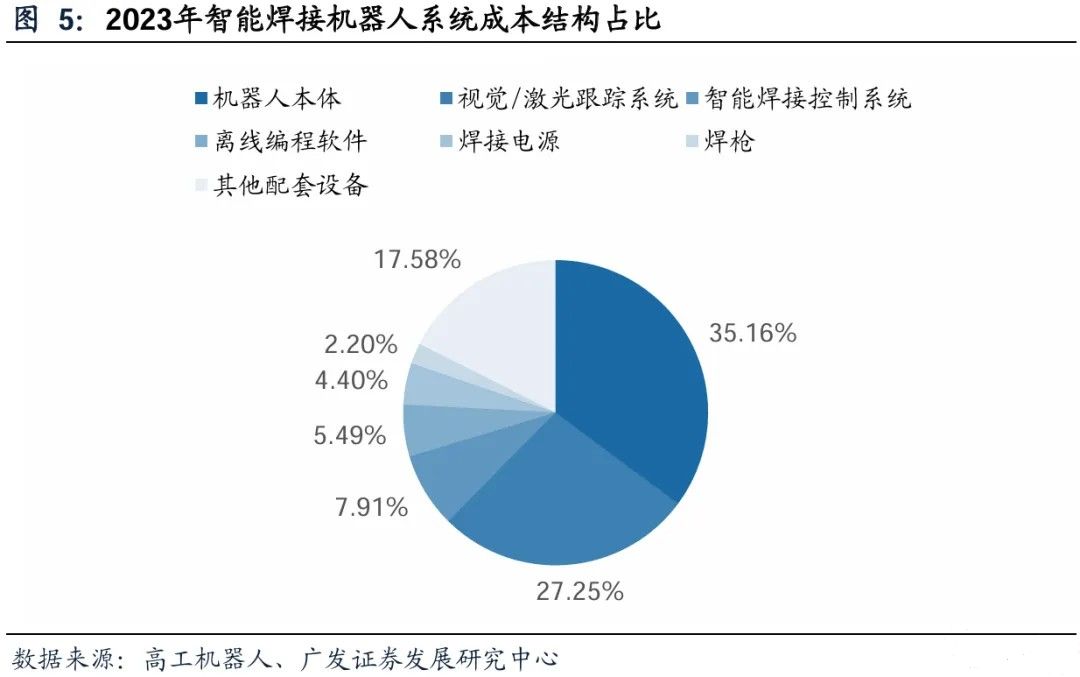
The intelligent welding robot industry chain consists of upstream component supply, midstream system integration, and downstream industry applications, all of which work together to promote industry development. As a highly automated welding equipment, intelligent welding robots integrate advanced technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, machine vision, sensor technology, and automation control. Among them, the robot body and vision/laser system occupy the core cost. According to statistics from high-tech robots, in the cost structure of intelligent welding robot systems in 2023, the total proportion of robot body and vision/laser system exceeds 60%.
Upstream enterprises mainly provide key components such as robot bodies, intelligent welding control systems, weld seam tracking systems, welding guns, welding power supplies, and offline programming software, which determine the performance and stability of the equipment. The robot body and intelligent control system form the foundation of intelligence. Domestic welding power supply manufacturers such as Megmeet have been leading the market for many years with stable performance. Welding gun sub categories are differentiated into MIG/MAG, TIG and other types according to process requirements. 3D vision and laser sensing technology improve welding accuracy through real-time correction, and structured light cameras and laser triangulation have become mainstream solutions. In the field of offline programming software, local manufacturers are breaking through foreign monopolies and lowering the threshold for automation transformation for small and medium-sized enterprises.
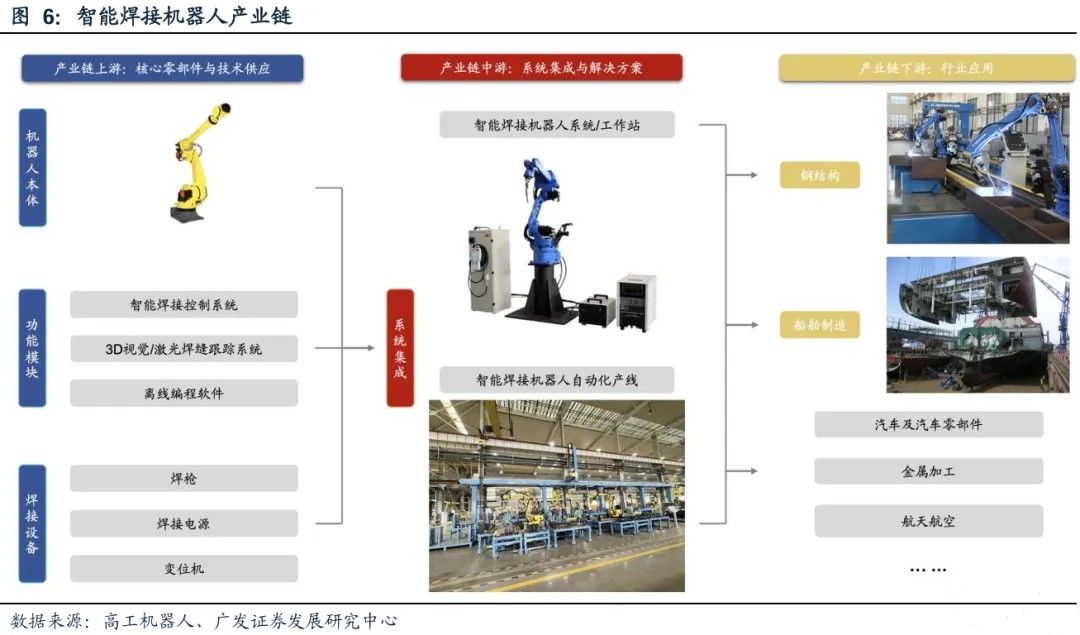
Midstream integrators are responsible for integrating intelligent welding robots and related equipment to form welding automation solutions that can be applied to different industrial scenarios. Welding robot workstations are suitable for industries such as steel structures and shipbuilding, while intelligent welding production lines meet the needs of large-scale and continuous production. Compared to traditional welding robots, intelligent welding robots require higher technical support in the integration process, involving fields such as sensor technology, machine vision, offline programming, and artificial intelligence. Local manufacturers are deeply engaged in intelligent path planning, with industrial robot intelligent operating systems as the core technology, providing robot intelligent workstations and intelligent work islands, and providing full process intelligent applications for the non-standard metal structure manufacturing industry.
Intelligent welding robots have shown great potential in downstream application scenarios. Traditional applications are concentrated in steel structures and shipbuilding, but with technological advancements and rising cost pressures, they are gradually penetrating into high-end manufacturing fields such as automobiles, metal processing, new energy, and aerospace. Against the backdrop of a shortage of welders and rising labor costs, intelligent welding robots are increasingly regarded by manufacturing companies as the core equipment for improving efficiency, reducing risks, and stabilizing production quality.